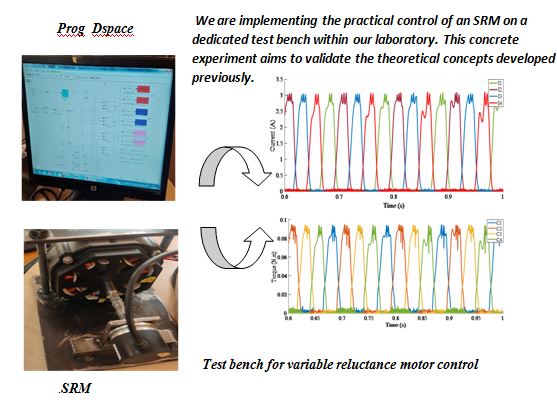
Experimental implementation of an SRM control approach
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.69717/jaest.v5.i2.144Keywords:
Experimental Realization- Real-Time Implementation- Switched Reluctance Motor (SRM)- current control strategyAbstract
This paper presents an improved current control strategy for a switched reluctance motor (SRM) drive. Owing to its doubly salient structure and nonlinear magnetic characteristics, the SRM exhibits strong coupling between current, flux, and torque, making accurate current regulation essential for achieving stable torque production and minimizing acoustic noise and ripple. The proposed controller is designed to enhance current tracking accuracy under fast dynamic conditions while preserving robustness against magnetic saturation, inverter delays, and load disturbances. Experimental validation is conducted on a fully instrumented SRM test bench using real-time acquisition hardware and a standard asymmetric bridge converter. The study demonstrates significant improvements in current tracking, torque quality, energy utilization, and global operational reliability when measured against earlier approaches in the literature.
Highlights
- Significantly improved current-tracking performance with reduced dynamic error.
- Enhanced torque quality, including lower ripple and smoother torque production.
- Increased overall energy efficiency of the drive system.
- Improved operational reliability compared to conventional controllers reported in previous studies.
- The proposed solution outperforms existing methods in terms of accuracy, robustness, and overall performance.
Downloads
References
G. Fang, F. P. Scalcon, D. Xiao, R. P. Vieira, H. A. Grundling, and A. Emadi, Advanced Control of Switched Reluctance Motors (SRMs): A Review on Current Regulation, Torque Control and Vibration Suppression, IEEE Open Journal of the Industrial Electronics Society, 2 (2021) 280–301. https://doi.org/10.1109/OJIES.2021.3076807.
H. Li, Q. Wei, L. Zhang, and N. Li, Suppression of Torque Ripple in Switched Reluctance Motors Which is Based on Synchronization Technology, EAI Endorsed Transactions on Energy Web, 11 (2021) 5802. https://doi.org/10.4108/ew.5802.
M. van Meer, G. Witvoet, and T. Oomen, Robust Commutation Design: Applied to Switched Reluctance Motors, arXiv preprint, Feb. 2024. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2402.01216.
S. Ingolikar and A. S. Sindekar, Realization of Current Controlled Mode for Linear and Non-Linear Model of SRM Along with Torque Ripple Reduction, International Journal of Engineering Research & Technology (IJERT), 1 (2012) 1-5. https://doi.org/10.17577/IJERTV1IS7288.
R. Inanç and V. Ozbulur, Torque Ripple Minimization of a Switched Reluctance Motor by Using Continuous Sliding Mode Control Technique, Electric Power Systems Research, 66 (2003) 241–251. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-7796(03)00093-2.
Y. Zhu, M. Yao, X. Sun, A Review on Predictive Control Technology for Switched Reluctance Motor System, World Electric Vehicle Journal, 14 (2023) 221. https://doi.org/10.3390/wevj14080221.
L. Henriques, L. Rolim, W. Suemitsu, P. J. Costa Branco, and J. A. Dente, Torque Ripple Minimization in a Switched Reluctance Drive by Neuro-Fuzzy Compensation, IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, 36 (2000) 3592 - 3594. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.cs/0010003.
H. Alharkan, S. Saadatmand, M. Ferdowsi, and P. Shamsi, Optimal Tracking Current Control of Switched Reluctance Motor Drives Using Reinforcement Q-learning Scheduling, IEEE Access, 9 (2021) 9926-9936. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3050167.
B. Soliman, Torque Ripples Reduction and Speed Control of a Switched Reluctance Motor Based on Artificial Intelligence Techniques, International Journal of Power Electronics and Drive Systems (IJPEDS), 16 (2025) 936–948. https://doi.org/10.11591/ijpeds.v16.i2.pp936-948.
L. Wang, K. T. Lionel, P. Chen, and L. Yang, Parameter Identification of Nonlinear Flux-Linkage Model for Switched Reluctance Motor Based on Chaotic Diagonal Recurrent Neural Network, Journal of Engineering Science and Technology Review, 17 (2024) 157–164. https://doi.org/10.25103/jestr.172.16.
A. Arif, A. Guettaf, A.C. Megherbi, et al. Electromagnetic modeling and control of switched reluctance motor using finite elements. Frontiers in Energy, 8 (2014) 355–363. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11708-014-0319-5.
A. Guettaf, F. Chabane, A. Arif, S. Benramache, Dynamic Modeling in a Switched Reluctance Motor SRM using Finite Elements, Journal of Power Technologies, 93 (2013) 149-153. https://doi.org/10.25103/jestr.172.16.
A. Arif, A. Guettaf, S. Sbaa, S. Benramache, Electromagnetic characteristics correlated with the excitation current and the rotor position in the SRM. International Journal of System Assurance Engineering and Management, 8 (2017) 180–187. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13198-015-0366-2.
K. Youghourta, G. Abderrazak, A. Arif,6/4 SRM electromagnetic modeling and control by using Finite element method. 3rd International Conference on Electrical, Communication and Computer Engineering, ICECCE 2021 12–13. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICECCE52056.2021.9514120.
A. Xu, C. Shang, J. Chen, et al. A New Control Method Based on DTC and MPC to Reduce Torque Ripple in SRM. IEEE Access 7 (2019) 68584–68593. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2917317.
H. Kotb, A.H. Yakout, M.A. Attia, et al. Speed control and torque ripple minimization of SRM using local unimodal sampling and spotted hyena algorithms based cascaded PID controller. Ain Shams Engineering Journal 13 (2022) 101719. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asej.2022.101719.
L. Han, A. Xu, J. Zhu, W. Zhang, Torque Observer of SRM Based on BP Neural Network Optimized by Bat Algorithm, 22nd International Conference on Electrical Machines and Systems, ICEMS (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICEMS.2019.8921967.
X. Sun, J. Wu, G. Lei, et al. Torque Ripple Reduction of SRM Drive Using Improved Direct Torque Control with Sliding Mode Controller and Observer. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics 68 (2020) 9334–9345. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIE.2020.3020026.
Ž, Ferková, Ľ. Suchý, P. Bober, Comparison of 6/4 and 12/8 switched reluctance motor models using direct torque control with torque lookup table. Electrical Engineering 102 (2020) 75–83. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00202-019-00775-z.
Z. Xu, T. Li, F. Zhang, et al. A Review on Segmented Switched Reluctance Motors. Energies 15 (2022) 9212. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15239212.
S. Han, K. Diao, X. Sun, Overview of multi-phase switched reluctance motor drives for electric vehicles. Advances in Mechanical Engineering 13 (2021) 1–18. https://doi.org/10.1177/16878140211045195.
G. Fang, F. PinarelloScalcon, D. Xiao, et al. Advanced Control of Switched Reluctance Motors (SRMs): A Review on Current Regulation, Torque Control and Vibration Suppression. IEEE Open Journal of the Industrial Electronics Society 2 (2021) 280–301. https://doi.org/10.1109/OJIES.2021.3076807.
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Journal of Applied Engineering Science and Technology

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
This journal provides immediate open access to its content on the principle that making research freely available to the public supports a greater global exchange of knowledge.
All articles are published under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (CC BY 4.0), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are properly credited.
License URL: https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/