Study of the Hydrodynamic performance Membranes based on the Polysulfone and doped Polyanilibe : Conception and application
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.69717/jaest.v5.i2.136Keywords:
Membrane, Polysulfone, Polyaniline, Water treatmentAbstract
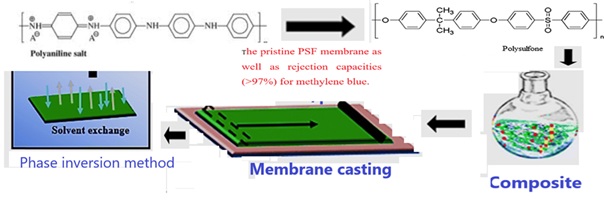
Polysulfone/polyaniline ultrafiltration ((PSF/PANI-UF) membranes were prepared via the phase inversion method using six examples of the polyaniline (PANI) synthesized in the presence of doped by functionalized agent dopants by direct process. To enhance the hydrodynamic performances of these prepared membranes, the conducting polyaniline (PANIs) has been added at different mass compositions (0.0, 0.2, 0.5 and 1.0%). The performance surface hydrophobicity was estimated by the contact angle. The PSF/PANI Membranes were characterized by FTIR spectroscopy in order to identify the interaction between PSF, PEG and PANI in presence of NMP solvent. The UV-Visible results of the PANIs pellets indicate that PANIs were obtained as emerald salt, which confirmed by calculating the oxidation state of PANIs from the FTR spectra. The separation properties of the composite membranes were studied in terms of water permeability and methylene blue removal. The porosity and the permeability of the membranes PFS/PANI were improved in comparison with that of the pristine PSF membrane as well as rejection capacities (>97%) for methylene blue. In addition to this, the pure water flux of the membrane (PANI (B and D)) increased reaching up to 0.0444 and 0.05824-ml. min-1 respectively at a pressure of 3.0 bars.
Highlights
- Composites based on different doped PANIs prepared using the reverse phase method.
- The percentages of the different formulations were carefully considered.
- Several techniques were proposed to confirm the presence of the dopant in the structure of PANI and polysulfone.
- The techniques were used to study the performance of the developed membranes.
- The results obtained confirmed the usefulness of the developed membranes in the field of wastewater purification, especially methylene blue.
Downloads
References
R.P. Scharzenbach, T.Egli, T.B.Hofstetter, B.Wehli, Global Water Pollution and Human, Annual Review of Environment and Resources 35 (2010) 109 – 136.
H. R. Safavi, S. Enteshar, Conjunctive use of surface and ground water resources using the ant system optimization, Agricultural Water Management, 173 (2016) 23-34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2016.05.001.
S. Peng, X. Lai, Y. Du, Y. Li, K. Tian, Y. Gan, Prevalence and Associated Factors for Depressive Symptomatology in Chinese Adults During COVID-19 Epidemic, Front. Psychol., 11 (2020) 616723. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2020.616723.
R.P. Lively, D.S. Sholl, From water to organics in membrane separations, Nat. Mater. 16 (2017) 276-279. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmat4860.
T. Huang, M. Alyami, N.M. Kashab, S.P. Nunes, Engineering membranes with macrocycles for precise molecular separations, J. Mater. Chem. A 9 (2021) 18102-18128. https://doi.org/10.1039/D1TA02982G.
J. Guo, Q. Yang, Q.-W. Meng, C.H. Lau, Q. Ge, Membrane Surface Functionalization with Imidazole Derivatives to Benefit Dye Removal and Fouling Resistance in Forward Osmosis, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 13 (2021) 6710-6719. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.0c22685.
G.M. Shi, Y. Feng, B. Li, M.T. Hui, T.S. Chung, Recent Progress of Organic Solvent Nanofiltration Membranes, Prog. Polym. Sci. 123 (2021) 101470. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.progpolymsci.2021.101470.
S. Zhang, L. Shen, H. Deng, Q. Liu, X. You, J. Yuan, Z. Jiang, S. Zhang, Ultrathin Membranes for Separations: A New Era Driven by Advanced Nanotechnology, Adv. Mater. 34 (2022) 2108457. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.202108457.
X. Shi, Z. Zhang, S. Fang, J. Wang, Y. Zhang, Y. Wang, Flexible and Robust Three-Dimensional Covalent Organic Framework Membranes for Precise Separations under Extreme Conditions, Nano Lett. 21 (2021) 8355–8362. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.nanolett.1c02919.
Amos Bick, Gideon Oron, Assessing the Intake and the Pretreatment Design of Reverse Osmosis Seawater (ROSW) Plants Using Analytical Hierarchical Process (AHP), Conference: 6th IWA Specialist Conference on “Membrane Technology for Water & Wastewater Treatment”, Aachen, Germany (2011).
B. S. Lalia,V. Kochkodan, R. Hashaikeh, N. Hilal, A review on membrane fabrication: structure, properties and performance relationship, Desalination 326 (2013) 77-95. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2013.06.016.
H. Guo,Y. Wyart, J. Perot, F. Nauleau, P. Moulin, Low-pressure membrane integrity tests for drinking water treatment : Review, Water Res. 44 (2010) 41–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2009.09.032.
J. H. Kim, K. H. Lee, Effect of PEG additive on membrane formation by phase inversion, J. Membr. Sci. 138 (1998) 153-163. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0376-7388(97)00224-X.
K. Toyomoto, A. Higuchi, Microfiltration and Ultrafiltration, Marcel Dekker, New York, 289 (1992).
J.A. Koehler, M. Ulbricht, G. Belfort, Intermolecular forces between a protein and a hydrophilic modified polysulfone film with relevance to filtration, Langmuir 16 (2000) 10419–10427. https://doi.org/10.1021/la000593r.
J. V. Tupe , S.M. Khot, D. Padmanabhan, B. Rajaguru, Polysulfone membranes with natural additives for water purification: Fabrication and performance testing, Polymer, 338 (2025) 129070. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymer.2025.129070.
Hanan S. Fahmy, Ragab Abouzeid, M. S. Abd El-sadek, G. T. Abdel-Jaber, W. Y. Ali, Hamouda M. Mousa, Fabrication of polysulfone membranes by blending with polyaniline and cellulose nanocrystals: towards the effective separation of oil-in-water emulsions, journal Applied Nanoscience, 30 (2023) 5871–5893. https://doi.org/10.1134/S2070205124701715.
M. N.l Naseer , K. Dutta, A. A. Zaidi , M. Asif , A. Alqahtany, N. A. Aldossary , R. Jamil, S. H. Alyami , J. Jaafar, esearch Trends in the Use of Polyaniline Membrane for Water Treatment Applications: A Scientometric Analysis, Membranes, 12 (2022) 777. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12080777.
M. Wang, L.G. Wu, J.X. Mo, C.J. Gao, The preparation and characterization of novel charged polyacrylonitrile/PES-C blend membranes used for ultrafiltration, J. Membr. Sci. 274 (2006) 200-208. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2005.05.035.
H.T. Yeo, S.T. Lee, M.J. Han, Role of polymer additive in casting solution in preparation of phase inversion polysulfone membranes, J. Chem. Eng. Jpn. 33 (2000) 180-185. https://doi.org/10.1252/jcej.33.180.
F. Amadoa, L. Rodrigues Jr., M. Rodrigues, A. Bernardes, J. Ferreirab, C. Ferreiraa, Development of polyurethane/polyaniline membranes for zinc recovery through electrodialysis, Desalination 186 (2005) 19-206. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2005.05.019.
H. Lee, S. Yang, Synthesis and characterization of polyaniline/silica doped with camphorsulfonic acid and dodecylbenzylsulfonic acid, J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 116 (2010) 934-945. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.31624.
W. Zhong, X. Chen, S. Liu, Y. Wang, W. Yang, Synthesis of highly hydrophilic polyaniline nanowires and sub-micro/nanostructured dendrites on poly(propylene) film surfaces, Macromol. Rapid Commun. 27 (2006) 563–569. https://doi.org/10.1002/marc.200500796.
S. Zhao, Z. Wang, J.X. Wang, S.B. Yang, S.C. Wang, PSf/PANI nanocomposite membrane prepared by in situ blending of PSf and PANI/NMP, J. Membr. Sci. 376 (2011) 83–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2011.04.008.
J. Li, M. Zhou, J. Lin, W. Ye, Y. Xu, J. Shen, C. Gao, B. Van der Bruggen, Monovalent cation selective membranes for electrodialysis by introducing polyquaternium-7 in a commercial cation exchange membrane, Journal of Mmebrane Science 486 (2015) 466– 471. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2014.12.056.
J. Li, H. Wang, X. Yuan, J. Zhang, J.W. Chew, Metal-organic framework membranes for wastewater treatment and water regeneration, Coord. Chem. Rev. 404 (2020) 213116, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2019.213116.
N Sekkak a, A Masb, M Berrada , A El Harfi , F Schue, Membranes polysulfone et polysulfone modifié pour la deshydratation de l'éthanol par pervaporation, 37 (2001) 1543-1551. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0014-3057(01)00037-4.
L Geng, Y. Zhao, X.Huang, S. Wang, S. Zhang, S. Wu, Characterization and gas sensitivity study of polyaniline/SnO2 hybrid material prepared by hydrothermal route, Sensors and Actuators B 120 (2007) 568–572. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2006.03.009.
J. Yan, T. Wei, Z. Fan, W. Qian, M. Zhang, X. Shen, F. Wei, Preparation of graphene nanosheet/carbon nanotube/polyaniline composite as electrode material for supercapacitors, J. Power Sources 195 (2010) 3041–3045. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2009.11.028.
http://terathane.invista.com/e-trolley/page_10324/index.html: Uses of PTMEG polyols. Retrieved (2007).
http://www.intermediates.basf.com/chemicals/spandex/global-player, BASF Corporation, USA: Global Player and Local Presence. Retrieved (2014).
L C. Mendes, A.P.S. Falco, M.S. Pinho, P.O. Marques, Sulfonated polyaniline: influence of sulfonation routes on its thermal and structural characteristics, Mater. Res. 14 (2011) 466-471. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1516-14392011005000070.
A.P. Kobzev, J. Huran, D. Maczka, and M. Turek, Vacuum, 83 (2009) S124. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vacuum.2009.01.042.
A. AJFAR, Ulvan as A New Trend in Agriculture, Food Processing and Medicine 6 (2020) 47–54. https://doi.org/10.9734/ajfar/2020/v6i430105.
P.V. Witte, P.J. Dijkstra, J.W.A. Van den Berg, J. Feijen, Phase separation processes in polymer solutions in relation to membrane formation, J. Membr. Sci. 117 (1-2) (1996) 1-31.
Veerababu, Polisetti, Vyas, Bhavik B. , Singh, Puyam S. , Ray, Paramita, Limiting thickness of polyamide-polysulfone thin-film-composite nanofiltration membrane, Desalination, Volume 346 (2014) 19-29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2014.05.007.
Blanco J.F, Sublet J, Nguyen Q.T, Schaetzel P. Journal of Membrane Science 283 (2006) 27–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2006.06.011.
“WHO Model List of Essential Medicines », Technical document,word hearth organisation (2021) 22nd list,
Rafizah W.A.W, Ismail A F. Effect of carbon molecular sieve sizing with poly(vinyl pyrrolidone) K-15 on carbon molecular sieve–polysulfone mixed matrix membrane, Journal of Membrane Science 307 (1) (2008) 53-61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2007.09.007.
J E Mark. Polymer Data Handbook. OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS, ISBN 0195107896 / 0-19-510789-6, (1999) 949-955.
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Journal of Applied Engineering Science and Technology

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.